What is RJ45 Color Code and Why Is It Important?
The RJ45 color code refers to the standard arrangement of wires within an RJ45 connector, commonly used for Ethernet cables. The RJ45 connector follows an 8-position, 8-contact (8P8C) design and requires precise wiring to ensure proper signal transmission.
These color codes for RJ 45 plugs are essential for organizing the individual wires into a specific order, helping to prevent electrical interference and ensure consistent communication. This is especially crucial for Power over Ethernet (PoE) applications, where data and power are transmitted simultaneously, with certain pins allocated to carry power and others for data.
The RJ45 cable color code is not just about organization. Having a clearly defined color code system simplifies cable identification, reduces errors during installation, and can even impact the performance of data transmission. For example, adhering to the correct color code prevents crossed wires, ensuring optimal signal quality and minimizing data loss.
Standards of RJ45 Connector Color Code: T568A and T568B
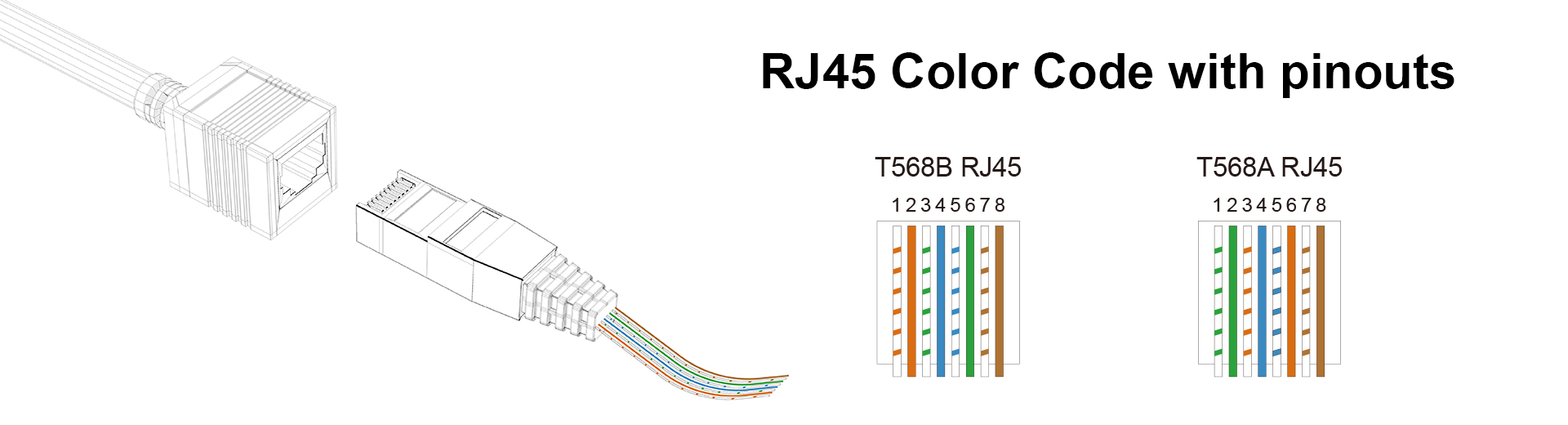
There are two widely recognized color code standards for RJ45 cable wiring: T568A and T568B, both used to arrange the color-coded pairs in Ethernet cables like Cat6. Each color in these standards represents specific functions within the cable, determining data transmission paths. The striped ones are always odd-numbered pins and solid-colored ones are even-numbered pins.
In both T568A and T568B, the White/Blue (Pin 4), Blue (Pin 5), White/Brown (Pin 7), and Brown (Pin 8) wires serve a similar role. These pairs are typically unused for data transmission in standard Ethernet cables but play an important role in Power over Ethernet (PoE) setups, providing power to devices such as security cameras and VoIP phones. If PoE is not being used, these pairs may remain idle but provide critical support in commercial applications.
The primary difference between T568A and T568B lies in the swapping of the green and orange wire pairs. In T568A, the green pair is responsible for transmitting data, while the orange pair handles receiving. In T568B, this is reversed, with the orange pair transmitting and the green pair receiving. These standards are important for ensuring consistent wiring in Ethernet networks and avoiding miscommunication between devices, especially when using different standards on opposite ends of a cable.
T568A Color Code Table
|
Pin Number |
Color Code |
Signal |
Description |
|
1 |
White/Green |
Transmit + (Tx +) |
Transmits data |
|
2 |
Green |
Transmit - (Tx -) |
Transmits data |
|
3 |
White/Orange |
Receive + (Rx +) |
Receives data |
|
4 |
Blue |
Unused/PoE |
Used for Power over Ethernet (PoE) |
|
5 |
White/Blue |
Unused/PoE |
Used for Power over Ethernet (PoE) |
|
6 |
Orange |
Receive - (Rx -) |
Receives data |
|
7 |
White/Brown |
Unused/PoE |
Used for Power over Ethernet (PoE) |
|
8 |
Brown |
Unused/PoE |
Used for Power over Ethernet (PoE) |
T568B Color Code Table
|
Pin Number |
Color Code |
Signal |
Description |
|
1 |
White/Orange |
Transmit + (Tx +) |
Transmits data |
|
2 |
Orange |
Transmit - (Tx -) |
Transmits data |
|
3 |
White/Green |
Receive + (Rx +) |
Receives data |
|
4 |
Blue |
Unused/PoE |
Used for Power over Ethernet (PoE) |
|
5 |
White/Blue |
Unused/PoE |
Used for Power over Ethernet (PoE) |
|
6 |
Green |
Receive - (Rx -) |
Receives data |
|
7 |
White/Brown |
Unused/PoE |
Used for Power over Ethernet (PoE) |
|
8 |
Brown |
Unused/PoE |
Used for Power over Ethernet (PoE) |
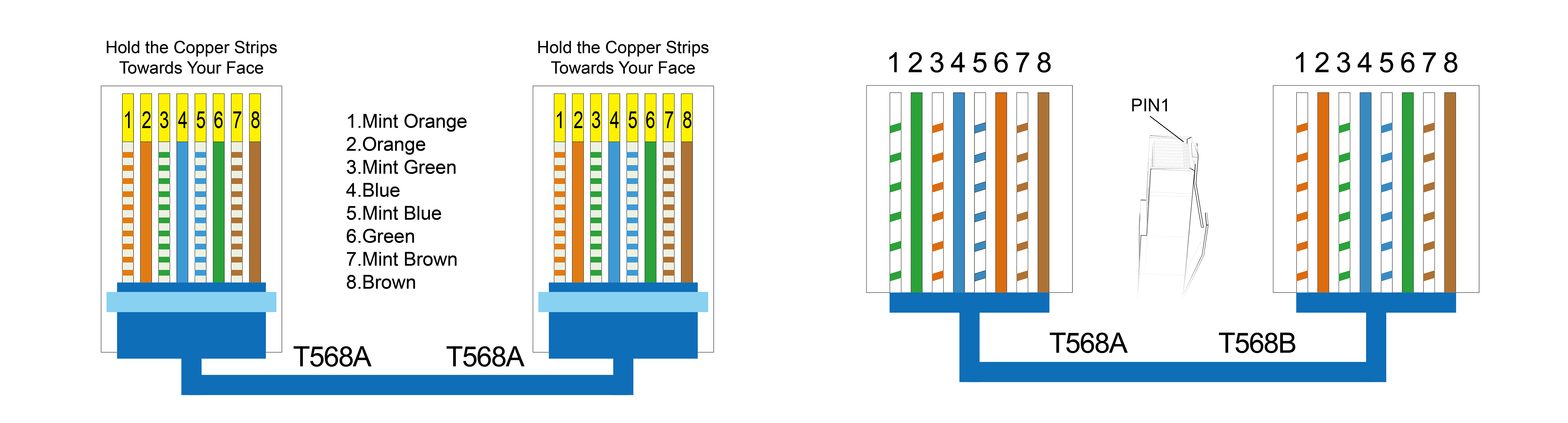
Moreover, the way these wires are connected at each end of the cable defines two common configurations: straight-through and crossover pinouts. These pinouts determine how data is transmitted between devices, ensuring proper communication across your network.
For Straight Through
This configuration is used to connect different types of devices, such as a computer to a router or switch. In a straight-through cable, both ends are wired using the same color code standard, either T568A or T568B. This means the pin assignments are identical at both ends, allowing for direct communication between devices with different roles in the network (e.g., sending and receiving data).
For Crossover Pinout
This configuration is used for connecting similar devices, such as two computers or two switches, directly without an intermediary device (like a router). In a crossover cable, one end is wired using the T568A standard, and the other end uses the T568B standard. This arrangement ensures that the transmit and receive wires are "crossed" so that the transmitting pins on one end connect to the receiving pins on the other, facilitating communication between the two devices.
Should You Use T568A or T568B?
When deciding between RJ45 Color Code A or B, the choice largely depends on compatibility with existing infrastructure and regional preferences. T568A is often used in environments that require backward compatibility with older systems, such as legacy telephone networks or government installations, commonly seen in Europe and the Pacific region. It is the preferred choice when projects involve older systems or require federal compliance due to its backward compatibility with older telecom systems.
On the other hand, T568B is more widely adopted in modern commercial and residential networks, aligning better with contemporary equipment and making it the default standard in most telecom installations, particularly in the United States.
For most setups, consistency is crucial. If you're expanding an existing network, it's best to stick with the current wiring standard. However, for new installations, T568B is often recommended due to its widespread use and better alignment with modern systems. Lastly, keep in mind that for straight-through cables, use the same standard at both ends, while for crossover cables, mix T568A and T568B to ensure proper data transmission.
Need High-Quality RJ45 Connectors? MSL Is Your Go-To Manufacturer
Understanding the RJ45 color code is crucial for creating reliable Ethernet cables that ensure smooth data transmission. Whether you use the Color Code A or Color Code B standard, consistency in wiring is key for ensuring network compatibility and avoiding connectivity issues. Straight-through cables are used for connecting different devices, while crossover cables connect similar devices, with the wiring arrangement adjusted accordingly to facilitate communication.